Quick Sort
Quick sort is one of the most widely used and efficient sorting algorithms. It is a divide and conquer technique, that means, we divide a problem into sub-problems and then solve them accordingly.
This sorting algorithm includes selecting a pivot point and finding its appropriate place in the array by putting elements smaller to it on its left side, and the elements greater than it to its right side. We then create a partition around this correct position of pivot.
This process of creating a partition is the backbone of the Quick Sort algorithm.
It is to be noted that any element can be selected as the pivot, but we have to proceed accordingly. In our case we will use the first element of Array as pivot element.
Understanding Quick Sort
Firstly we can select the pivot point in the following ways:-
- Select the first element as pivot point
- Select the last element as pivot point
- Select median element as the pivot point
- Select any other element as the pivot point
Then we find the index where this pivot should be present in the sorted array.
The array is then partitioned around this pivot, and recursive calls are made to the left and right sub-arrays following the same procedure, that is, selecting the pivot point and finding its correct place in the sorted array.
We can divide the algorithm into two parts, one will be the responsible for partitioning the array and finding the correct position of the pivot, while the other part will be responsible for placing recursive calls to the left and right sub-arrays accordingly.
Now let’s look at the detailed algorithm.
Partitioning Algorithm
- Select the first element as pivot point
- Take two integers
i&jthat point to low and high of the array respectively - Increment the value of
iuntilArray[i]is less than pivot - Decrement the value of
juntilArray[j]is greater than pivot - Swap
Array[i]andArray[j] - If i and j pass each other, that is,
i > j, swap pivot andArray[j]
Now, this pivot is the correct place for this element in the array.
Quick Sort Algorithm Steps
- Call partition method: partition (Array, low, high)
- Make recursive call to the left sub-array: quickSort( Array, low, partition-1)
- Make recursive call to the right sub-array: quickSort( Array, partition+1, high)
- Continue this until high is greater than low.
Example
Consider an Array: 6 4 13 7 5 17 8
We select Array[0] => 6 as the pivot, and take two pointers i and j.
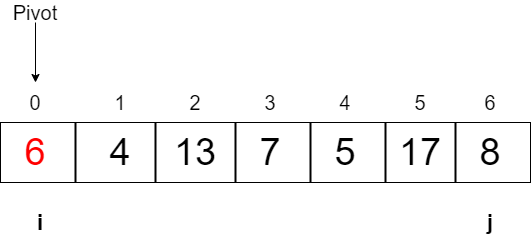
Now we will increment the value of i until the value at i is less than the pivot, and decrement the value of j until the value at j is greater than the pivot.
i=0, j=6, pivot=6 (Array[0])
Array[i]=6, which is equal to the pivot
i++
i=1
Array[i]=4, which is less than the pivot
i++
i=2
Array[i]=13, which is greater than the pivot
loop exit
value of i = 2
Array[j]=8, which is greater than the pivot
j--
j=5
Array[j]=17, which is greater than the pivot
j--
j=4
Array[j]=5, which is less than the pivot
loop exit
value of j = 4
Now we will swap Array[i] and Array[j],that is, Array[2] and Array[4]Now the array will look like
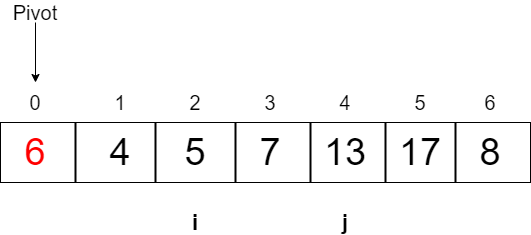
Again we will follow tha same procedure until value of i is less than j.
i=2, j=4, pivot=6
Array[i]=5, which is less than pivot
i++
i=3
Array[i]=7, which is greater than pivot
loop exit
value of i = 3
Array[j]=13, which is greater than pivot
j--
j=3
Array[j]=7, which is greater than pivot
j--
j=2
Array[j]=5, which is less than pivot
loop exit
value of j=2
Note that now j < i, so we will exit from loop
Now we will swap pivot and Array[j], this makes pivot placed in its correct position with elements smaller in its left side, and elements greater on the right side.The array now looks like:
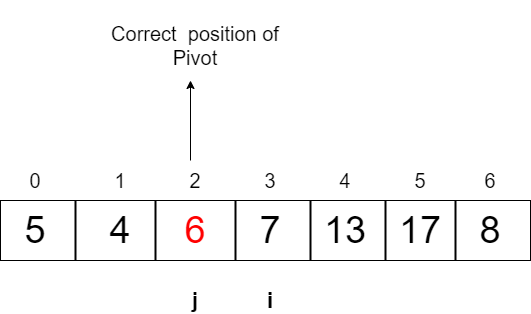
Now the array is partitioned around the pivot.
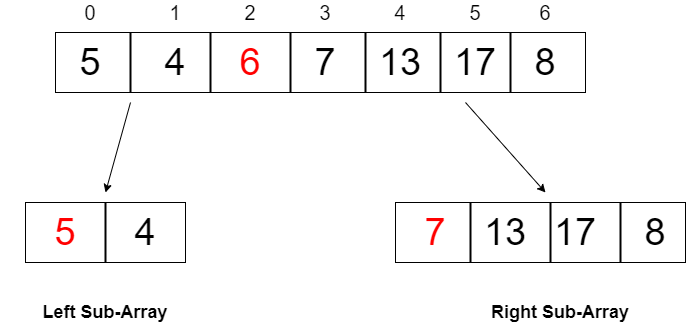
Once we get the partitioning done, same process is followed recursively on the left and right sub-arrays, which makes every element placed in their correct positions.
The tree will look as follows:-
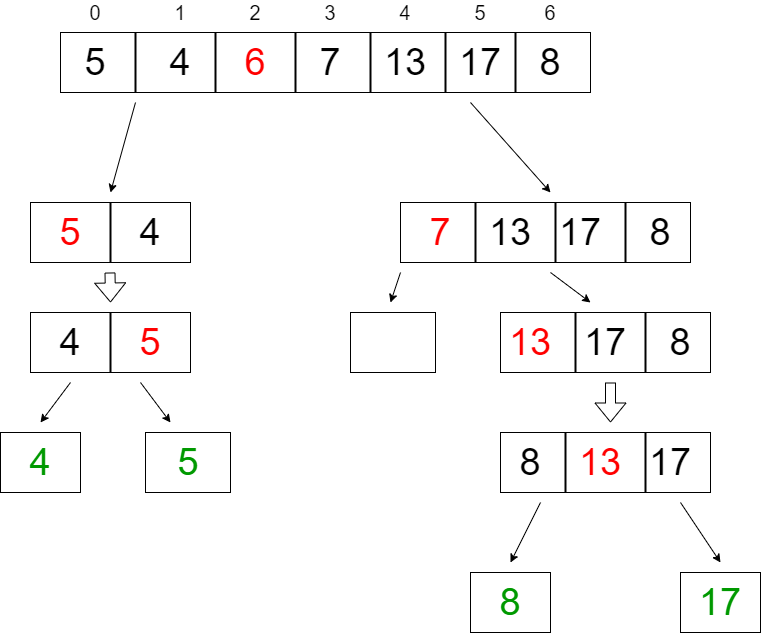
Now let’s have a look at the code for Quick Sort.
Quick Sort Code
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Sorting {
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[low]; // selecting first element as pivot element
int i = low;
int j = high;
int temp; // temporary variable for swapping
while (i < j) {
while (arr[i] <= pivot) {
i++;
}
while (arr[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
//swapping
if (i < j) {
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
arr[low] = arr[j];
arr[j] = pivot;
return j;
}
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int locationOfPivot = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, locationOfPivot - 1); // recursive call to left sub-array
quickSort(arr, locationOfPivot + 1, high); // recursive call to right sub-array
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sorting sort = new Sorting(); // creating object of class Sorting
int[] arr = { 9, 14, 6, 1, 7, 11, 3, 5 };
sort.quickSort(arr, 0, 7); // method call
System.out.println("Array after applying Quick Sort: " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}Performance
| Case | Runtime |
|---|---|
| Best | O(nlogn) |
| Average | O(nlogn) |
| Worst | O(n^2) |
| Space complexity | O(n) |
Since quick sort is a recursive algorithm, therefore it requires a stack for computation and hence the space complexity O(n).
Help us improve this content by editing this page on GitHub