Heap Sort
Sorting as you might already know is basically an algorithm that is used for arranging elements of a list in a certain order. (Usually ascending or descending). Sorting is one of the most important categories of algorithms, it can significantly reduce the complexity of problems, and is generally used for efficient searching.
There are an ample number of sorting algorithms available like the Bubble sort, Selection sort, Insertion sort, Merge sort, Quick sort, Heap sort, Counting sort and more. The type of algorithm to choose depends on the type of problem. (Generally Merge Sort and Quick sort are used.)
Today we will be discussing Heap Sort. Now before directly jumping to Heap Sort, we must be aware of a few terminologies.
1. Complete Binary Tree
We can define a complete binary tree as a tree in which every level is completely filled except possibly the last, and it is as left as possible.
2. Binary Heap
A binary heap is a complete binary tree in which the value of parent is greater or lesser than its children.
If the value of parent is greater than its children, then it’s called max-heap else we call it min-heap.
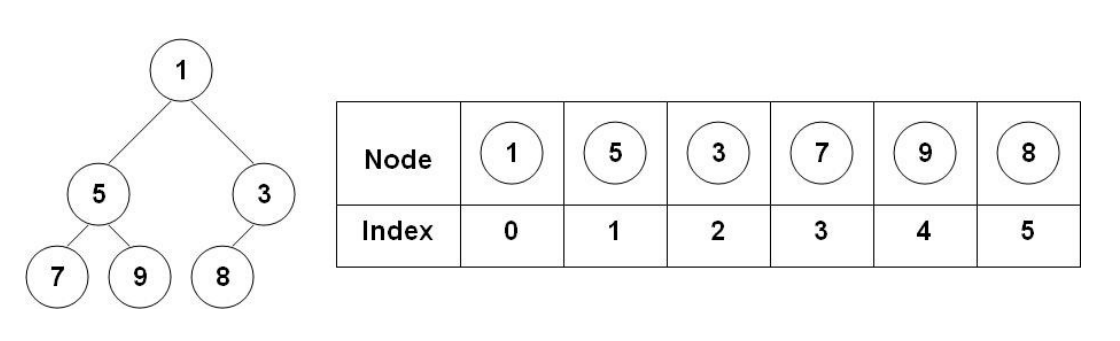
We can represent the heap as a binary tree or an array.
Array Representation of Heap:
As we have already discussed that heap is a type of complete binary tree, therefore it is easy to represent it as an array.
Let’s suppose that the parent node is at index i
Then the left child will be at (2 * i) + 1
And the right child will be at (2 * i) + 2
Examples
Parent index= 0Left child index= 2*0 + 1 = 1Right child index= 2*0 +2=2
Parent index= 1Left child index= 2*1 + 1 = 3Right child index= 2*1 +2=4
Parent index= 2Left child index= 2*2 + 1 = 5Right child index= 2*2 +2=6
HeapSort
Heap sort algorithm is a comparison based sorting technique, it’s basic working is similar to that of insertion sort. It is an in-place sorting algorithm but is not stable, that is, the original order of keys is not maintained.
Understanding the algorithm
In the heap sort algorithm, we insert all the elements from the unsorted list or array into a heap. We then create max-heap which brings the largest element at the root of the heap, we exchange this value with the last value and then decrement size of the array. Then, we heapify the first element. This process is continued until there is only one element left in the array.
Java Code for Heap Sort
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Sorting {
public void heapSort(int arr[]) {
int lengthOfArray = arr.length;
// creating heap
for (int i = (lengthOfArray - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arr, lengthOfArray, i);
}
// Sorting
for (int i = lengthOfArray - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Swap the root node with last node
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[0];
arr[0] = temp;
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
public void heapify(int[] arr, int index, int i) {
// Initializing parent and children
int parentIndex = i;
int leftChild = (2 * i) + 1;
int rightChild = (2 * i) + 2;
// comparing the left child value
if (leftChild < index && arr[leftChild] > arr[parentIndex]) {
parentIndex = leftChild;
}
// comparing the right child value
if (rightChild < index && arr[rightChild] > arr[parentIndex]) {
parentIndex = rightChild;
}
if (parentIndex != i) {
int temp = arr[parentIndex];
arr[parentIndex] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
heapify(arr, index, parentIndex); // recursive call
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[]) {
Sorting sort = new Sorting();
int[] arr = {
46,
76,
24,
1,
9,
7,
11,
38,
79,
13
};
sort.heapSort(arr);
System.out.println("Array after applying heap sort is " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}The above program will generate the following output:
Array after applying heap sort is [1, 7, 9, 11, 13, 24, 38, 46, 76, 79]Performance of Heap Sort
- Worst case time complexity:
O(nlogn) - Best case time complexity:
O(nlogn) - Average case time performance:
O(nlogn) - Worst case space complexity:
O(n) - Auxiliary space complexity:
O(1)
Help us improve this content by editing this page on GitHub