Bucket Sort
We saw how Counting Sort sorts elements in linear time, another such sorting technique is Bucket Sort and is an improvised version of the same.
In this algorithm we create buckets within a certain range and assign elements accordingly, after this we apply some sorting technique to sort elements in buckets.
Understanding Bucket Sort Algorithm
The given array is divided into buckets and then these buckets are sorted individually.
Now we gather these buckets in order which gives us the required sorted array.
The buckets we create can be sorted by using any sorting technique, but generally, we prefer Insertion Sort. We can also call the bucket sort method recursively to sort the bucket elements.
Bucket Sort Algorithm
- Create N buckets each denoting a certain range
- Initialize each bucket with zeroes
- Read elements from the array and put them into their respective bucket according to range
- Sort each bucket individually
- Coagulate buckets in order
Bucket Sort Example
Consider an Array : 38, 27, 67, 59, 46, 7, 18, 5, 55, 64
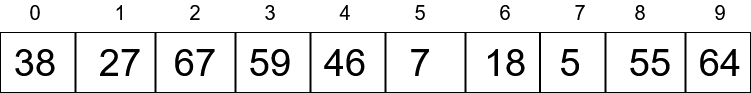
Our first task will be to create buckets, and for finding out how many buckets we need, we use the below formula, you can also use any other method.
Number of Buckets = (Maximum element - Minimum Element)/10 + 1
= (67-5)/10 + 1
= 7 (7.2 will be rounded off to 7)In this case, 7 buckets will be created.
After the buckets are created our main motive is to assign elements in the appropriate bucket.
min = 5
i = 0 to Length of Array
i = 0
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (38-5)/10
= 3
38 will be assigned to 4th bucket (3 is the index)
i = 1
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (27-5)/10
= 2
27 will be assigned to 3rd bucket
i = 2
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (67-5)/10
= 6
67 will be assigned to 7th bucket
i = 3
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (59-5)/10
= 5
59 will be assigned to 6th bucket
i = 4
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (46-5)/10
= 4
46 will be assigned to 5th bucket
i = 5
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (7-5)/10
= 0
7 will be assigned to 1st bucket
i = 6
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (18-5)/10
= 1
18 will be assigned to 2nd bucket
i = 7
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (5-5)/10
= 0
5 will be assigned to 1st bucket
i = 8
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (55-5)/10
= 5
55 will be assigned to 6th bucket
i = 9
Bucket = (Array[i] - min)/10
= (64-5)/10
= 5
64 will be assigned to 6th bucket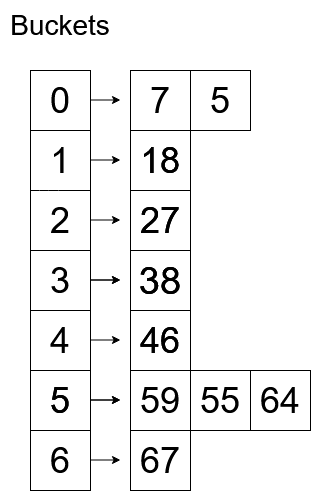
After the buckets are assigned, Insertion Sort will be applied to each bucket, after that, we will merge all the buckets in order.
This is how the buckets will look after sorting.
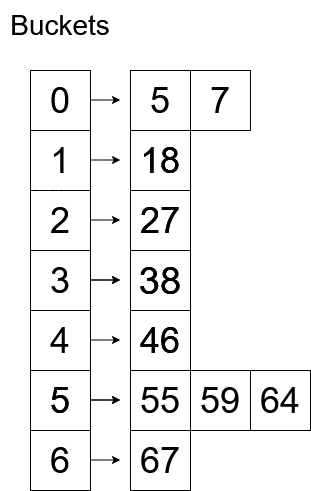
The sorted array will look like:

It has to be noted that buckets can be created using any method, and any of the sorting technique can be applied.
Now let’s have a look at code for the same.
Code for Bucket Sort
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Sorting {
void bucketSort(int arr[], int max, int min) {
int lengthOfArray = arr.length;
int numberOfBuckets = (max-min)/10 + 1 ; // Number 10 can be adjusted according to range required
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> buckets = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfBuckets; i++) {
buckets.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < lengthOfArray; i++) {
buckets.get((arr[i] - min) / 10).add(arr[i]);
}
int k=0; // To get result array index
for(int i =0; i<buckets.size();i++) {
Integer bucket[] = new Integer[buckets.get(i).size()];
bucket = buckets.get(i).toArray(bucket);
insertionSort(bucket);
for(int j=0;j<bucket.length;j++) {
arr[k++]= bucket[j];
}
}
}
void insertionSort(Integer[] bucket) {
int lengthOfArray = bucket.length; // Length of input array
int value; // to store current element
int pos; // to store position of current element
for (int i = 1; i < lengthOfArray; i++) {
pos = i - 1;
value = bucket[i];
while (pos >= 0 && bucket[pos] > value) {
bucket[pos + 1] = bucket[pos];
pos = pos - 1;
}
bucket[pos + 1] = value;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sorting sort = new Sorting(); // creating object of class Sorting
int arr[]= {38,27,67,59,46,5,18,7,55,64}; //5,9,2,13,11
sort.bucketSort(arr,67,5); // method call
System.out.println("Array after applying bucket sort : " + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}Performance
| Case | Runtime |
|---|---|
| Best | O(n) |
| Average | O(n+k) |
| Worst | O(n^2) |
| Auxiliary Space | O(n+k) |
Bucket sort should be preferred when the elements are uniformly distributed and the number of elements is not very large.
Help us improve this content by editing this page on GitHub